We all have heard success stories of enterprise resource planning (ERP) (click for presentation) software in different organisations. But a great number of ERP installations fail. Gartner mentions that about 75% of all ERP implementations fail .. Why is it that these implementations fail, even after committing so much of human resources, material resources, money, time etc to the project.
 No study of ERP systems is complete unless we make an earnest attempt to understand why ERP systems fail.
No study of ERP systems is complete unless we make an earnest attempt to understand why ERP systems fail.
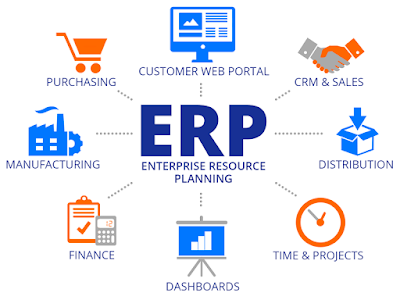
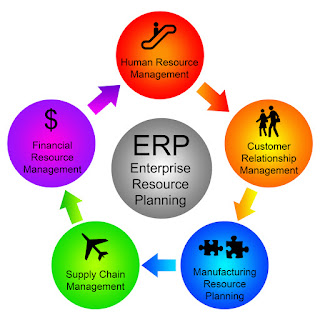
Though ERP systems are just a collection of basic RDBMS software that connects all the departments in an organisation to help in the smooth functioning of the organisation, maintain integrity of data, enable secure access of this centralised data, with a smooth software interface connecting the user, the customer, the server storing the centralised data, the implementation, upkeep and maintenance of the ERP system is very challenging.
 I had my first experience on RDBMSs with Ingres working on mini computers, then came Unisys, ( both at Goa Engineering College) and Oracle. Oracle now remains one of the top RDBMS sofware in the industry, mainly because of its reach and ability to convince customers of its user friendliness.
I had my first experience on RDBMSs with Ingres working on mini computers, then came Unisys, ( both at Goa Engineering College) and Oracle. Oracle now remains one of the top RDBMS sofware in the industry, mainly because of its reach and ability to convince customers of its user friendliness.
In the free and open source software domain, we have two great RDBMSs , PostgreSQL and MySQL. MySQL was formerly powering Facebook but of late has been purchased by Oracle and to the best of my knowledge killed so that it would not be a competition to Oracle, the small commercial business package.
 RDBMSs form the basic component of any ERP package and SAP is now one of the most popular, widely used ERP software of the world.
RDBMSs form the basic component of any ERP package and SAP is now one of the most popular, widely used ERP software of the world.
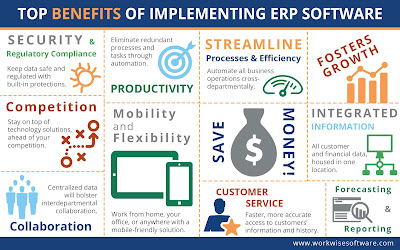
It makes better sense to study about any system by first having a general understanding of the system and then what are its drawbacks. The links given here are examples of failures or weaknesses of ERP packages and what could be done to overcome them.
Most of failure of ERP systems have taken place due to improper implementation. Let us look at what are the essential six phases of any ERP implementation. In the Big Bang approach, the different stages of implementation are done serially and then in a big bang it is brought in line in a short period of time. This implementation process is very risky.
 Organisations frequently go for the iterative approach where the implementation is done phase by phase with important departments in the organisation. The transition is slow and incremental. The advantage of this approach is that the errors in the implementation (inevitably there will be many) are progressively discovered and attended to, one at a time, so that the system does give a surprise to the organisation and keeps serving the basic interests of the customer and organisation and other stakeholders on a limited scale initially and then maturing to an advanced state later on.
Organisations frequently go for the iterative approach where the implementation is done phase by phase with important departments in the organisation. The transition is slow and incremental. The advantage of this approach is that the errors in the implementation (inevitably there will be many) are progressively discovered and attended to, one at a time, so that the system does give a surprise to the organisation and keeps serving the basic interests of the customer and organisation and other stakeholders on a limited scale initially and then maturing to an advanced state later on.
Most of failure of ERP systems have taken place due to improper implementation. Let us look at what are the essential six phases of any ERP implementation. In the Big Bang approach, the different stages of implementation are done serially and then in a big bang it is brought in line in a short period of time. This implementation process is very risky.
 Organisations frequently go for the iterative approach where the implementation is done phase by phase with important departments in the organisation. The transition is slow and incremental. The advantage of this approach is that the errors in the implementation (inevitably there will be many) are progressively discovered and attended to, one at a time, so that the system does give a surprise to the organisation and keeps serving the basic interests of the customer and organisation and other stakeholders on a limited scale initially and then maturing to an advanced state later on.
Organisations frequently go for the iterative approach where the implementation is done phase by phase with important departments in the organisation. The transition is slow and incremental. The advantage of this approach is that the errors in the implementation (inevitably there will be many) are progressively discovered and attended to, one at a time, so that the system does give a surprise to the organisation and keeps serving the basic interests of the customer and organisation and other stakeholders on a limited scale initially and then maturing to an advanced state later on.
Top 5 reasons why ERP implementations fail and what one can do about it .. Click here ..
A student report from UT Dallas on why ERP systems fail.. click here ..
ICMR case on ERP Failure at HP ..
george..










No comments:
Post a Comment